Share this
The Definitive Guide: What is Innovation?
by Anna Crona
The interest in innovation is snowballing, and it has never been more critical for companies to embrace innovation. Grasping ”the innovation area” and start taking concrete action can, however, feel overwhelming. So, we wanted to give you our way to describe innovation.
Whether you are a full-blown innovation professional or just starting, if you are driving practical innovation projects or if you as a CEO want to understand the innovation process dynamics and learn about why you should invest in innovation - This is the guide for you!
In this guide, you will, among other things, learn about what innovation is, start understanding the different types of innovation and how they work, and get insight into why innovation is crucial for companies wanting to stay competitive over time.
What is innovation?
There are many different definitions of innovation, so what is the meaning of innovation in english? These are some of them:
- "Innovation, in its modern meaning, is "a new idea, creative thoughts, new imaginations in the form of device or method." - Wikipedia, 2020
- "The word innovation comes from the Latin word "innovare", which means renew." - Wikipedia, 2020
- "Innovation is a new idea, for example, a product, solution, business idea, service, chemical formula, mathematical method or technology, that turns out to be promising or working." - Wikipedia, 2020
- "Innovation is about new or better solutions that create value for society, companies, and individuals." - Regeringen.se, 2020
- "Innovation is our main tool to renew and create new values." - Innovationsledarna, 2020
What is an innovation?
Describing innovation in these ways implies that just because something is new or not yet known, it is not innovation unless it also creates value for several people. Hence, the conclusion would be that for something to be called innovation, it needs to be (1) NEW, and it needs to (2) create VALUE. Using this definition would separate that which is only new (an invention) or only creates value (what we may call optimization or streamlining), from innovation. This tells us that for something to be innovation, it must successfully spread to people who can extract its value.
New & Valuable - The concept of innovation
What does it mean to work with new things that create value, then? Well, things that are new and not yet known will be challenging to define and predict the effects of. We just don't know what we will end up with and what the impact of implementing it will be. Developing something that creates value for several people, on the other hand, means two things. We need to (1) reach enough people, and (2) make sure that what we have created is relevant and valuable to them.
Creating value for a group of unknown people, from something new we cannot predict the effects of, puts innovators in a position of considerable uncertainty. Partly because it is very difficult to break the procedure of "driving innovation" into pieces and plan it in set steps. Therefore, we need to adopt a way of working that allows us to learn from each activity we perform and use the learnings to form the next step - not too far from a "learning-by-doing" method.
Why do we need to define and separate innovation from other activities then? Well, doing so allows us to let go of the "same old" models, structures, and best practices that we have been using for decades. Instead, we can find new ways of working that are suitable for driving innovation.
Only when we admit that innovation is different from other types of work can we shape the conditions and our efforts accordingly and find our way of driving innovation. Only then can we successfully discover, develop, and implement our next core business.
Innovation vs. Operations
Most established companies are very accomplished at running their current core business. The processes are optimized, the customer offer is perfectly refined, and all internal structures are streamlined towards getting the most out of the existing business. These organizations are experts in delivering this specific value to their customers. We call the activity of refining our current core business "core business operations".
Working with innovation is about doing something for the first time [further discussed in What is innovation?]. This is utterly different from performing core business operations. We are not optimizing something existing or refining something we already know, but rather creating something new. Hence, the structures and processes we have been perfecting for core business operations are probably not suitable for innovation work. But why?
"Yet to be discovered"
Working with innovation is about finding and realizing something new. We are concerned with "Why?", "For who?" and "What?". core business operations, however, is mostly focused on "How?". How will we execute on this core business project? The vital difference is that when we are working with innovation, we do not know what the end goal is - that is yet to be discovered. Therefore, we need to use a purpose and problem statement as the basis for our efforts (instead of a concrete end goal) [further discussed in Vision->Strategy->Scope], and keep on doing things and learn from every discovery. Thereby we create the end goal along the way. When working with core business operations, on the other hand, we can break down the known end goal into pieces and create an optimized process for achieving it.
"The vital difference is that when we are working with innovation, we do not know what the end goal is - that is yet to be discovered."
These differences make up very different conditions for innovation projects in comparison to other types of projects. Innovation projects are defined by their high level of uncertainty and low level of predictability. In contrast, core business projects are generally predetermined and therefore quite certain and predictable - because we have already decided what we are going to achieve.
The risk of investing in projects with as high uncertainty as innovation projects is enormous in comparison to investing in projects with a known end goal. Therefore, we need to use a different investment tactic when working with innovation. We start small, with only the amounts of resources required to iterate fast and with low precision, and learn quickly about the potential outcomes of the project. The more we learn, the more we lower the risk, the more we can increase the precision and investment - or terminate the project.
High level of uncertainty demands different competences
It may be uncomfortable, but we need to invest (if so only with our time) to learn and develop innovation projects. Further, the high level of uncertainty demands quite a lot from the people who drive organizational innovation efforts. They need to be able to shift between different competence areas and abstraction levels in order to lower all the risks and develop all the areas of the innovation project. This work requires them to be able to evaluate the relevance and potential of a project objectively, and decide if they believe it will create value for the target group and can be implemented, or if it should be terminated. To do so, they need a broad range of competences, and the energy to keep up their motivation under these very uncertain terms. Further, they need to stay away from falling in love with the solution they are investing their time and engagement in.
"We often fail at estimating the arrival of the "monster", since we think linearly and not exponentially. /../ Thus, you can't start acting too early!".
- Deloitte & Board Network, The Danish professional Directors Association
Core business operations projects are usually way more concrete. The outcomes are usually preplanned, and the risks are already assessed to be low enough to ensure a return on investment. Therefore, we already know where we are going and what needs to be done to get there - at least this is way more precise than in an innovation project. This results in a much lower level of uncertainty. As the project can be broken down into predetermined pieces, the people working in these projects can be experts within specific fields to ensure high quality. By keeping a high degree of coordination, we can assemble the result of what we have planned into a perfect realization of the predefined value.
Significant differences
Because of the significant differences between innovation- and core business projects, they cannot be planned, managed, measured, lead, or budgeted for in the same way. They cannot be benchmarked against each other with help from any standard metrics either. Therefore, it is not possible to compare or have them compete for the same resources within a company. An innovation project will never "win" in competition with another project if the metrics are, e.g. [ROI] or [Risk]. It will also be challenging to assess if an innovation project reached it's goals if the goals are based on the end result, as the end result was not known when the targets were set. This constitutes a significant challenge in ensuring resources early on for innovation efforts within established organizations who are only set up for managing core business projects.
"It will be challenging to assess if an innovation project reached it's goals if the goals are based on the end result, as the end result was not known when the targets were set."
It is important to remember that though innovation- and operation projects are different and require different conditions to flourish, they are both needed to make companies survive over time. If we cannot renew ourselves, we will become obsolete. If we cannot realize and exploit our current core business, we will not earn enough money to survive today and finance our efforts to have a competitive advantage over time.
Different types of Innovation
As long as it is new and creates value [further discussed in What is innovation?], innovation can be almost anything. We can however, categorize and name innovation to keep different types apart. No matter what we choose to call it or how we want to categorize, the most important thing is that we agree on a language we can all understand and use. Categorizing and separating different types of innovation from each other helps us to see the differences and adapt our efforts to fit our strategic goals.
One way of categorizing innovation is by using the labels "Continuous Improvement", "Incremental Innovation", "Radical Innovation", and "Disruptive Innovation". The differences between these terms are really how closely related to, or very different from, today's core business the innovation is. Working with Continuous Improvement, or Incremental Innovation, is working with new things which create value, and are strictly related to today's core business. Radical- or Disruptive innovation concerns new and valuable things that are not related to today's core business at all. Charles A. O'Reilly III and Michael L. Tushman are describing these categories and the dynamics of working with them in so-called 'Ambidextrous Organizations' in their HBR-article.
Continuous Improvement & Incremental Innovation
Continuous Improvement and Incremental Innovation are often close to what we usually call R&D, and is related to improving and renewing values we are already delivering. These projects are typically associated with a lower degree of the challenges connected to driving innovation [further discussed in Driving innovation projects], as they are easier to relate to and will do better in relation to the KPIs set up for today's core business compared to projects that does not have any relation to today's business.
Being crass, we could say that these categories should not even be called innovation, as they could be seen as a part of core business operations and R&D. However, Continuous Improvement and Incremental Innovation could also be viewed as one extreme on the scale of innovation. We could call them innovation projects on a lower level of abstraction, which is closer to implementation, and that relates to today's core business.
Radical- & Disruptive Innovation
Driving radical innovation is about creating completely new core businesses or new ways of working for the company. These projects are capable of disrupting a company's entire industry. The term "Disruptive" is not suitable for any innovation project that has not been realized yet as it implies that the innovation has disrupted and changed the conditions for, e.g. an entire market or product segment.
As we have no chance of predicting if this is going to happen before the innovation is released to the market, the term disruptive innovation is better used for innovations that have already been released, and become so widely spread in society that they have contributed to radical change or disruption.
One example of this could be the smartphone. Before the smartphone was introduced to the market, most people were carrying a telephone device in their hands. Afterwards, most of us are carrying a small computer instead. Now, no one wants to go back to holding only a telephone - hence, the market has been disrupted.
Radical innovation projects most often face all the challenges we associate with innovation, full on. Due to the high level of uncertainty [further discussed in Driving projects without a set end goal], and the fact that most established organizations are not adapted for promoting these types of projects, we need to actively create the conditions required to succeed [further discussed in Conditions for innovation].

Why use these categories?
Continuous Improvement, Incremental- and Radical innovation are usually facing very different degrees of uncertainty and resistance from a company. Therefore, we cannot fully compare them to each other. Incremental innovation projects have a relatively good chance of surviving and being implemented, even if the organization is not adapted for innovation. In contrast, radical projects have a statistically lower chance of succeeding. This is not due to that the radical projects generally provide less value, quite the opposite, but because they imply a considerably higher degree of uncertainty and challenge [further discussed in Innovation vs Operations]. If aiming to succeed in all categories, we need to start establishing the right conditions for the different categories within our companies.
Even though we separate these categories from each other, we must remember that one is no more important than the other. We need to work with innovations of all kinds to both refine the current core business and find our competitive edge for the next 2,5 or 10 years. By actively choosing to establish initiatives in all categories, acknowledging their differences, and creating the conditions they require to flourish, we can succeed with our innovation efforts over time.
In which areas can we drive organizational innovation?
As long as what we are developing is new and creates value for many people [further discussed in What is innovation?], it is innovation, no matter what area we are working in. In other words, it doesn't matter if an initiative aims to create a new value offer, if it develops a new way of working or introduce new values on a new market - it can still be innovative.
Hence, there is no limit to within which areas innovation can be driven. We can innovate around for example new business models, ways of working, products or services. There are models and frameworks we can use to extend our thinking about possible innovation areas. One example of this type of framework is ten types of innovation.
On top of this, innovation projects can have their starting point in any perspective (we can call it the base perspective), and there are some perspectives that all innovation projects need to take into consideration.
The base perspective for process innovation can have its foundation in for example the discovery of new customer needs, changes in a market, or the development of new technology innovation. These three bases can be called "need-based", "market-based" and "technology-based". The only difference is what perspective that constitutes the foundation for the innovation. This is important for two reasons:
1. Bring all perspectives
No matter which perspective that lay the foundation for the innovation, we still need to explore the other two to succeed. Discovering a fantastic opportunity in a new market will not create any value if what we are creating is not relevant to the users and customers in that market, or if the technology we use is outdated. Hence, we need to bring all perspectives into our innovation work [further discussed in Important innovation perspectives].
2. "The top 10 global innovators are 'need seekers'"
Innovation efforts that use the need-based perspective as a foundation seem to be more successful in general. Dave Power writes at harvard.edu that "Customer needs should drive innovation", Booz & Do states that 60 % of the top 10 global innovators are 'need seekers', and PwC writes that more than one-third of all companies say that the customers are their most crucial innovation partner. If this is true, we could actively choose to start our innovation efforts in need-based perspective and shape our innovation strategy towards becoming a needs seeker, and perhaps reach more successful innovation.
.png?width=400&name=PillarPage_1_%231%20(1).png)
These frameworks or check-lists can be utilized to develop creative ideas and innovations further, or to find previously unexplored areas to tap into. They can also help us focus our innovation efforts on specific areas by choosing some main areas for innovation. They are not meant to be used as rigid structures.
Why Innovation is essential
The expression "Innovate or die" can seem a bit drastic or excessive. However, it may be more widely used today than ever before. Over the years, there have been several companies who missed the "innovate-part", become obsolete, and thereby proved to us there is something to the expression. The most well known Swedish example may be Facit.
Most companies have an official purpose - something that states the reason for their existence and reflects the value they want to provide their customers with. However, earning money and maximizing profit also makes up for a substantial part of driving a company.
Without earning money, companies are not likely to be able to provide customers with value over time. Hence, making money becomes crucial for fulfilling the official, unique purpose that is stating the company's reason for existence.
Maximizing dividend today or staying relevant over time?
There are different ways to maximize profit. Companies can increase the price of what they are selling or try to reduce the cost of delivering and thereby increase profit. If successful, the next step is to prioritize between "earning money" and fulfilling the official purpose over time. Is the dividend or development of the company and value the highest priority?
If aiming to fulfill and develop the company's official value (and stay competitive over time), the company needs to spread their product/service/value to as many users and customers as possible. To achieve this, it is essential to develop and renew the product, service, or value as fast as, or faster, than the market is changing - or risk becoming obsolete and lose relevance for our users and customers. No commuter will buy a horse and carriage from you today, and you will not be able to sell accountants' analog calculation machines anymore. Hence, staying relevant by constant renewal and development is crucial to fulfilling our official purpose.
Innovation work aims at creating new things that provide value [further discussed in What is innovation?], which can be considered to be the best life insurance a company can get. Today, this is more relevant than ever before, as the speed of change is increasing, and the lifespan of large companies is decreasing [further discussed in Why is innovation so hyped?].
"Today, this is more relevant than ever before, as the speed of change is increasing, and the lifespan of large companies is decreasing."
Investing in innovation efforts is, of course, not mandatory. Companies can choose to discard the long term perspective and only maximize their short term dividend. However, to fulfill the official purpose AND be able to continue to make profits in the long run, innovation is essential in our ever-changing world. Without change, we risk becoming obsolete fast, and thereby lose our ability both to fulfill our purpose AND to do dividends.
Innovation Portfolio and Management
Supposing that we want to make money today and develop ourselves to stay relevant in the future, we need to distribute our investments over initiatives that aim to create value both now, in a year, and 5-10 years. Sorting initiatives into categories based on when we believe they will become implemented, and start providing value, we can get an overview of our potential competitive edge over time.
The famous "horizons"
If we want to distribute our initiatives over different time horizons, we also need to segment the future into blocks, or horizons. One way of doing this is by adopting the "3 horizons of innovation" that McKinsey created a while back. This model segments the future into three blocks based on time. However, we might argue that time is not the only perspective that is relevant for segmenting innovation initiatives. In his HBR-article, Steve Blanks describes that as the development speed today is so high that projects in the last horizon may be possible to implement earlier than the ones in the first horizon. If we agree with Blanks, we could segment the three horizons like this instead:
Horizon 1 - Innovations closely related to today's core value
Horizon 2 - Innovations related to today's core value, which are containing several new elements
Horizon 3 - Completely new innovations
The less related an initiative is to our current core business, the fresher it is for our company, the more uncertainty and difficulty in predicting the effects it will imply [further discussed in Innovation vs Operations].
Even though these horizons are segmented on "how new" something is, it could still be valuable and possible to add time as a perspective. Horizon 3 projects may be more likely to be implemented or terminated further into the future than horizon one projects.
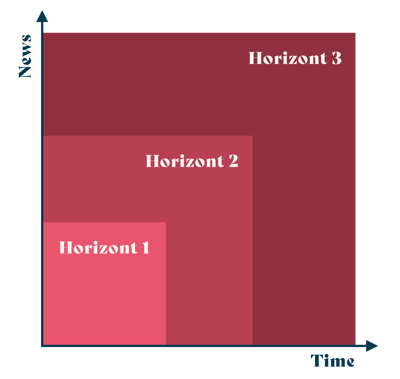
Finding your horizons
The time horizons will, however, differ greatly depending on the line of business the company is operating in. A company in the software industry is likely to have shorter time horizons than a company in the pharmaceutical industry.
Except for trying to assess the current potential of staying competitive over different time horizons, the horizon-model can be utilized to understand what phase specific projects are in - and thereby what support and which conditions it needs to succeed.
A project in horizon 1 is likely to be a Continuous improvement- or incremental innovation project. In contrast, a project in horizon 3 is more likely to be a radical innovation project [further discussed in Innovation vs Operations]. This knowledge helps us adapt to how we work with and manage each project, and it gives us a common language to communicate about the support that is needed. This enables us to adjust expectations in each phase and estimate the number of projects that are likely to reach the market, even if we cannot say which specific project it is going to be [further discussed in Vision->Strategy->Scope].
Segmenting our initiatives in this model helps us understand our current potential to renew our company. This means that the model can be the basis for our innovation portfolio, helping us sort out our strategic innovation work. By segmenting all initiatives over time, we can learn where we lack in innovation capability, where we need to add more initiatives and where projects seem to get stuck. This means that we can adopt strategic measures to steer our innovation portfolio in the desired direction and increase our chance of staying competitive over time. This is what we call innovation management.
Innovation cannibalize on our business!
Staying competitive over time means staying relevant both now and in the future [further discussed in Why innovation is essential] . Developing relevant businesses, ready for the future, does however demand time and resources during a time when the that business itself does not have any income at all. This will make that next business look unprofitable and force the current business to finance it.
Having an existing business financing prospective businesses is very normal, reasonable, and something companies should budget for [further discussed in Decision making and Budgeting]. Still, this way of prioritizing may feel non-intuitive if the company usually operates under the principle of having each department or initiative finance itself.
Innovation projects may, if implemented, also come to compete with the current core business. One example of this can be if the innovation efforts find a new, more relevant way of providing the same value that constitutes today's core business. If this happens, managers of the organization must make a strategic decision regarding if they should pursue the innovation or not. Will the existing business stay relevant when the innovation project enters the market? Can they coexist? When, if at all, will the innovation enter the market?
If you don't - your competitors will
Sometimes, the new solution should be implemented - maybe competitors will fill that market space if we don't. Sometimes, there is no reason to implement a new solution - if the need for a particular innovation is about to disappear, due to, e.g., a market disruption for example.
"We have to be prepared to cannibalize our businesses, and to change fast. Younger, more digital outside directors on board is one way for the board to keep close to the issues."
Another aspect that needs to be considered, related to that innovations can cannibalize on the existing business, is that the people who are working for and are experts within the existing business may lose their current positions if the new solution is implemented. These people may have worked on the existing core business for a long time and have all their knowledge and "status" wrapped up in this value offer. The fear of losing their position may make these people prone to resist innovation, even if it would be better for the company in general to implement it [further discussed in Conditions for innovation - Negative Emotions].
Why is Innovation so hyped?
There is a flurry of X-labs, innovation buzzwords and innovation consultants today, in a way that we have never seen before. But why is innovation so hyped? One explanation may be the increased speed of development that threatens to make companies obsolete [further discussed in The speed of development is the highest yet]. Today, more and more large companies are being outcompeted, while new actors are finding their way to growth.
It may also have to do with the organizational shift we stand before, where old best practices turn out not to be effective anymore [further discussed in The Shift: From production society to knowledge society]. One way of expressing it may be, "In an era of digital business and rapid technology change, virtually no company can ignore the imperative to innovate. Failing to do so is an invitation to lose business." - PWC.
Legacy vs. New & Fast
Trying to stay relevant by creating new values that are competitive in future markets implies that we have to start doing things we have never done before [further discussed in Driving projects without a set end goal]. We have to enter very uncertain grounds where we cannot predict and measure like we are used to [further discussed in Budgeting and Governance]. It forces us to work in new ways and find new ways to succeed.
Organizations built to maximize the value of their current business are usually not made for anything other than that. In addition, large, established companies are often struggling with their legacy, while watching new players grow very fast and start to outcompete them. How on earth can the new players, who never would have survived before, suddenly be so successful?
Succeeding with the innovation efforts has become something of a "secret sauce", and no one seems to know exactly how to manage it. This may well be because we are all looking for a management consultant to tell us what the best practice is. It may also be so that the perfect innovation organization or structure is yet to be discovered. Maybe the quick-fix does not exist.
Why should we even bother?
If there is no quick-fix to ensure that our innovation efforts are successful, and we cannot control and make sure the result will return our investments - why should we even bother? Is innovation yet another hyped craze that will soon blow over?
Maybe the word innovation will not be as buzzy and cool in a few years. Still, the development speed is not likely to decrease now when we have created the means for it to continue increasing. Therefore, we need to find our ways of learning about and developing our future competitive offers [further discussed in Why innovation is essential]. We need to do it in the same manner as when driving an innovation project by starting small and using a learning by doing-method [further discussed in What is innovation?].
The speed of development is the highest yet
"The speed of change is increasing". Maybe this feels counter-intuitive, maybe not. However, the truth is that there have been many massive technology innovation breakthroughs over the last years. And even if the speed of change would not be increasing, the belief that it does can contribute to the hype around innovation.
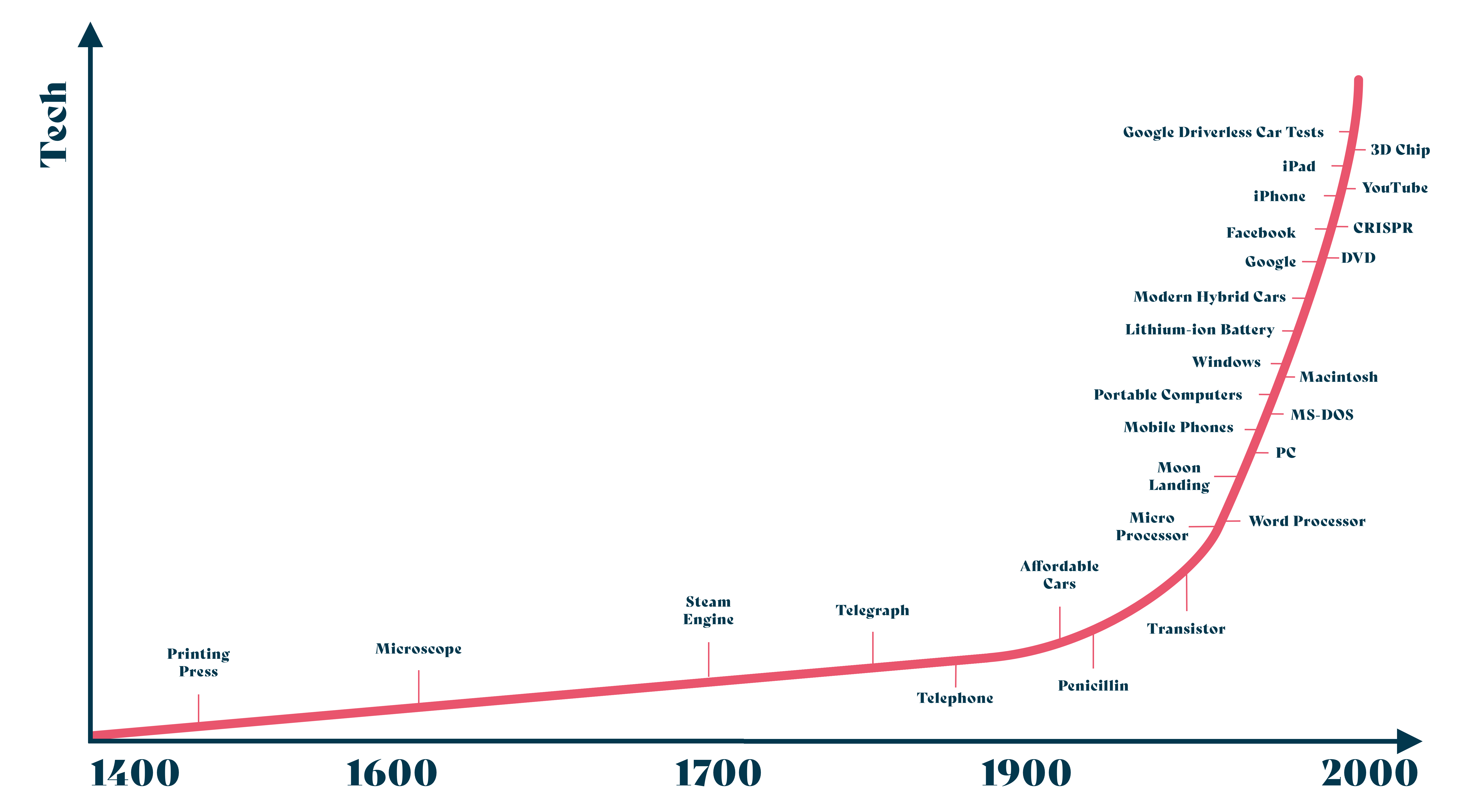
An innovation is something new that creates value [further discussed in What is innovation?]. This means that for something to be called innovation, it needs to be not previously known, and create relevant value for several people. This can be achieved, e.g. by spreading a new invention to enough people, whom it creates value for and having them pay for the invention. Having an invention is not enough to call ourselves innovative - there also needs to be a receptive market with customers and users.
It's a different world today
Succeeding with inventing and spreading something may have become easier for the individual in later years. Today, it is possible to create and spread something without having, e.g. a large production facility - it can be done digitally. All you need is a computer and you can reach almost the entire world. This technology shift has empowered new actors and given them access to a global network where they can spread their inventions, establishing a competitive landscape that is very different from the one dominating 50 or 100 years ago [further discussed in The shift: From production society to knowledge society].
Today, a small company with access to, and competence in, technology can outcompete a large established company. This is achieved by being faster and closer to their users, by reaching their customers using digital channels and by being more relevant for the current time. The advantage that technology provides becomes clear when looking at BCG's list of the most innovative companies in 2019, where all top companies are incorporating technology in their business. BCG is also describing the advantages of being a fast-moving company today.
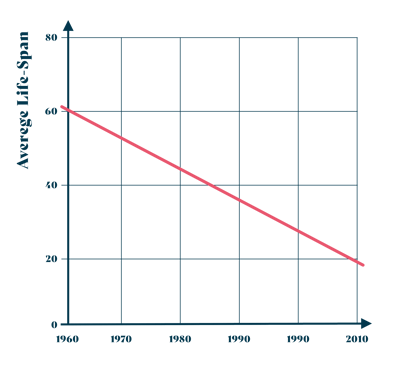
"McKinsey: We expect 75 % of the companies that exist today to have disappeared 2027"
The high development speed and the new competitive landscape have lead to a decrease in lifespan for large companies. Over the last 50 years, the average lifespan for the companies on the S&P 500 companies-list has decreased drastically (graph below). Statements from, e.g. McKinsey, saying that they expect 75 % of the companies that exist today to have disappeared 2027, or Deloitte writing "On top of this new bizz today is developed at a pace that leaves little time for thorough analysis and precise risk mitigation" are likely to also contribute to the innovation hype.
The shift: From production society to knowledge society
As the industrialization started, we entered the production society. In the production society, we worked in factories to manufacture something that someone had invented, which created enough value for people to pay for it. The factories employed people who assembled the products, and the operations were planned, controlled and optimized to maximize revenue.
The organizations were often built to allow the people at the top to delegate, condition, and manage the work. The workers were only supposed to do what they were told. Leadership was performed in a command-and-control-manner, and each manager was responsible for his or her workers and their performance.
Best Practice = Old Practices?
To increase the revenue or profit, the top management could optimize the process by looking for waste or loss in the production chain. As they were the only ones overlooking the entire process, they became the experts in value creation. There was much research done on what "best-practice" looked like during this time, and, i.e., Taylor and Ford made contributions with Scientific Management and the Assembly Line.
One discovery implied that workers would operate faster if they were only responsible for a small part of the manufacturing chain. Hence, workers were only taught how to perform a small part of the chain and were responsible for this bit only. The most critical resource in the manufacturing process became the workers' hands, and there was no need for them to think for themselves. They were only employed to use their hands to realize their small part of the production.
The only people who could drive development and maximize profit were the ones who knew the entire chain - top management. They were the ones that drove profit and value, and the ones that became irreplaceable. Many of today's organizations are developed from and inspired by this way of working. This is not strange, as this way of working has proved efficient in the past, and the research from Ford, Taylor, etc. is still influencing how we structure our organizations and ways of working.
The knowledge economy & economic growth
Today, we have moved on to the knowledge economy and production optimization is no longer the most significant driver of growth. Manfred M Fisher describes his view of the knowledge economy in "A systematic approach to innovation".
Today, it is no longer the companies that can optimize their production lines that grow the fastest and make the most money [further discussed in The speed of development is the highest yet], but the software-driven companies who scale their businesses by reaching many customers with their user-friendly apps and web pages. What drives their "production" is not hands, but their constant learning and collaboration aiming to create the best products and services for the customers of today.
This becomes clear when we look into and compare the revenue/employee of the new, technology-intensive companies, and the older companies with an organizational legacy. The comparison shows that the new companies have a much higher revenue/employee, indicating that they are better at utilizing their employees' knowledge and contribution.
Revenue/Employee

In the knowledge economy, it is no longer people's hands we are employing them for - it is their brains. We are dependent on having people "at the bottom of the organization" think for themselves. Suddenly, they are the experts at driving value and profit by learning about and developing the next business. Hence, top management needs to adopt an entirely new role and view of themselves, which creates some challenges for the traditional organization.
Challenges in shifting
Managers needs to adopt a very different role
In the traditional organization, managers are meant to tell people what to do and control that their workers perform according to the set goals. The manager is the person with the most knowledge; he or she has the most information, as he or she has the highest position in the organization. He or she has all the answers - how else could a manager control the workers? In the new type of organization, the manager needs to adopt a very different role. He or she is now supposed to create the right conditions for the employees to be able to utilize their brain power, and to have them design and develop new ideas. This without the manager being the expert, and without delegating, controlling and making all decisions [further discussed in Leading Innovators].
Coordinating knowledge
If we could have the guy at the top break down and delegate the tasks that needed to be done before, we today have to coordinate knowledge from different domains furthest down in the organization to find the next revenue stream. Suddenly the experts are scattered across the entire organization. The silos and command and control-structures that worked so well for delegation become an obstacle for collaboration. Because who knows someone in another silo? Who should get credit if we collaborate and create something great? And who should take the cost of the work?
We are dependent on a transparent culture
In an organization where each unit only reports its results upwards to show that they are doing a good job, there is little to gain from collaboration with other departments or companies. There is also nothing to be gained for management in being transparent with plans and visions. Employees only need to know their specific tasks and how they are controlled. Instead of transparency, this creates a culture of protecting information. Today, we are dependent on a transparent culture [further discussed in Conditions for Innovation]. How is an employee supposed to know how to make decisions if they do not know the company vision and goals, or how the decision can affect others' work? How are employees supposed to contribute with ideas that are relevant to a company they only know a small piece of?
We are learning as we go
All processes and structures in the production society are built to achieve a predetermined goal - making the product that has already been invented - with enough quality and without waste. In the new organization, we seldom know exactly what we are making from the start (at least not when working with innovation). Instead, we are learning as we go and define the end goal along the way, using trial and error [further discussed in Driving projects without a set end goal]. The structures built to delegate and control are not suited for that type of knowledge-driven work.
Shift in employee mindset
For employees to shift from receiving orders and deliver on something that was delegated to them to suddenly work with continuous learning and making their own decisions is a substantial change. It demands that employees are able to change how they view their role and that they can shift mindsets and between levels of abstraction (detailed and strategic level) [further discussed in Innovation vs Operations]. It also requires that the employees are willing to learn new things and dares contribute with their opinions and ideas.
Find ways of working
In the traditional organization, market- and product planning decided what was supposed to be manufactured over time. Those products were then designed, manufactured and released to the market. Today's companies must understand their needs and drivers, and dynamically work with developing products that create value for them. This forces companies to find ways of working that are much closer to the customer than they are used to, and try to predict how the market is going to evolve in the future, in order to understand what the next successful product will be. Traditional companies are usually not used to this way of working.
BCG describes how they see the shift from "the old to the new" and the "autoimmune reaction" it can create within companies.
These challenges indicate that the ways we used to organize ourselves in the production economy are not the best ways of organizing our companies in the knowledge economy. To stay competitive, we need to find new ways of organizing, structuring, and leading our organizations. This is, of course, much easier done for companies that don't have a built-in legacy from the production society. This advantage if of course exploited by many newly started companies, who utilize it to compete with large established companies. These new, legacy-free companies manage to compete with the old giants [further discussed in The speed of development is the highest yet], and it forces the older, more established companies to "jump onto the innovation train".
Related article: How to drive innovation
Share this
- Monday (1)
- Friday (1)
- Sunday (2)
- Friday (4)
- Tuesday (5)
- Saturday (2)
- Thursday (16)
- Monday (18)
- Saturday (9)
- Wednesday (15)
- Wednesday (5)
- Thursday (6)
- Tuesday (1)
- Tuesday (3)
- Tuesday (1)
- Wednesday (3)
- Monday (1)
- Friday (1)
- Sunday (1)
- Saturday (1)
- Sunday (1)
- Friday (1)
- Thursday (1)
- Thursday (1)
- Sunday (1)
- Tuesday (1)
- Saturday (1)
- Thursday (1)